Introduction
In recent years, the landscape of healthcare has undergone a seismic shift, driven by the integration of digital technologies. One of the most significant innovations reshaping healthcare delivery is the emergence of virtual hospital platforms. These platforms are revolutionising patient care by providing a convenient, effective, and easily accessible substitute for conventional in-person treatments. From real-time consultations to remote patient monitoring, virtual hospitals are transforming modern healthcare delivery in profound ways.
Definition
Virtual hospital platforms are digital healthcare systems that provide remote medical services using telemedicine, electronic health records, remote monitoring, and AI-powered tools. These platforms enable patients to receive consultations, diagnoses, treatments, and follow-ups from healthcare professionals without visiting a physical facility, improving access to care and enhancing efficiency in healthcare delivery.
What Are Virtual Hospital Platforms?
Digital ecosystems known as virtual hospital platforms allow medical practitioners to provide distant medical care. These platforms encompass a broad range of technologies, including video consultations, electronic health records (EHRs), remote diagnostics, wearable device integration, AI-powered health analytics, and telemonitoring tools.
Unlike traditional telemedicine – which is often limited to consultations – virtual hospitals offer a more comprehensive suite of services. They allow patients to obtain ongoing care from the convenience of their homes by simulating a real hospital setting. These platforms often support various departments such as cardiology, psychiatry, dermatology, and even intensive care units (ICUs).
Key Features of Virtual Hospitals
Several key features distinguish virtual hospital platforms from basic telehealth services:
- Multidisciplinary Care Teams: Virtual platforms bring together doctors, nurses, specialists, and care coordinators in a centralized digital space.
- Remote Monitoring: Through wearables and IoT devices, patient vitals can be monitored in real-time, enabling proactive intervention.
- Integrated Health Records: EHRs ensure seamless data sharing among providers, enhancing coordination and treatment accuracy.
- AI and Data Analytics: Predictive analytics and AI-driven tools help identify risks and optimize treatment plans.
- 24/7 Accessibility: Many virtual hospitals offer round-the-clock care, reducing the need for emergency room visits.
Benefits of Virtual Hospital Platforms
Improved Access to Care:
One of the most significant benefits of virtual hospital platforms is the elimination of geographic barriers. Patients in remote or underserved areas can consult with top-tier specialists without traveling long distances. This has an especially significant effect in areas with inadequate healthcare facilities.
Enhanced Patient Engagement:
Patients are empowered to manage their health more actively thanks to digital platforms. With easy access to their medical records, appointment scheduling, and virtual consultations, patients become more informed and engaged in their care journeys.
Cost-Effective Healthcare:
Virtual hospitals significantly reduce overhead costs associated with physical infrastructure, administrative staff, and in-person visits. This cost effectiveness is advantageous to patients as well as healthcare providers. Fewer hospital admissions and readmissions also translate to lower expenses for insurance companies and government health systems.
Timely Medical Interventions:
Continuous remote monitoring enables medical professionals to quickly identify and address any early indicators of a patient’s condition worsening. Hospital readmission rates can be decreased, problems can be avoided, and results can be improved with this proactive strategy.
Better Management of Chronic Diseases:
Chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension require ongoing care and monitoring. Virtual platforms provide a structured environment for chronic disease management, offering features like medication reminders, diet tracking, and regular teleconsultations with specialists.
Use Cases in Real-World Settings
COVID-19 Pandemic Response:
Virtual hospital systems were quickly used as a result of the COVID-19 epidemic. With hospitals overwhelmed and the need for social distancing, virtual care became essential. Countries like the U.S., UK, and India launched nationwide virtual care initiatives that helped manage mild to moderate cases at home while preserving hospital resources for severe cases.
Remote Intensive Care Units (eICUs):
Some virtual hospitals have developed remote ICUs, where critical care physicians can monitor patients using real-time data from hospital equipment. These eICUs extend critical care expertise to smaller or rural hospitals that may lack on-site intensivists.
Mental Health Services:
Mental health platforms integrated into virtual hospitals have greatly improved access to therapy and counseling. Patients facing anxiety, depression, or PTSD can now receive timely support through confidential video sessions, often with shorter wait times compared to traditional clinics.
Challenges and Considerations
While virtual hospital platforms offer numerous advantages, they are not without challenges.
Digital Divide:
Not every patient has the required digital gadgets or dependable internet connectivity. This creates a disparity in who can benefit from virtual care, particularly affecting elderly populations or those in low-income communities.
Data Privacy and Security:
With sensitive medical data being transmitted and stored online, robust cybersecurity measures are essential. Providers must comply with data protection regulations such as HIPAA (in the U.S.) or GDPR (in Europe) to safeguard patient information.
Licensing and Regulation:
Cross-border virtual care introduces complexities around medical licensing and jurisdiction. A physician licensed in one state or country may not be authorized to treat a patient in another, limiting the scalability of virtual platforms.
Clinical Limitations:
Not all medical conditions can be effectively managed remotely. Some diagnoses and treatments still require physical examination, laboratory tests, or surgical intervention. Therefore, virtual hospitals are best seen as a complement to, rather than a replacement for, traditional care.
The Future of Virtual Hospitals
The future of virtual hospital platforms looks promising, with continued advancements expected in areas such as:
- AI-Driven Diagnostics: Enhanced by machine learning, virtual hospitals will increasingly rely on AI to assist in diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR): These technologies could enable virtual physical therapy sessions or immersive medical education.
- Interoperability Standards: As systems become more integrated, seamless communication between virtual and traditional care settings will improve continuity of care.
- Global Health Access: Virtual hospitals have the potential to democratize healthcare by extending high-quality medical services to underdeveloped regions worldwide.
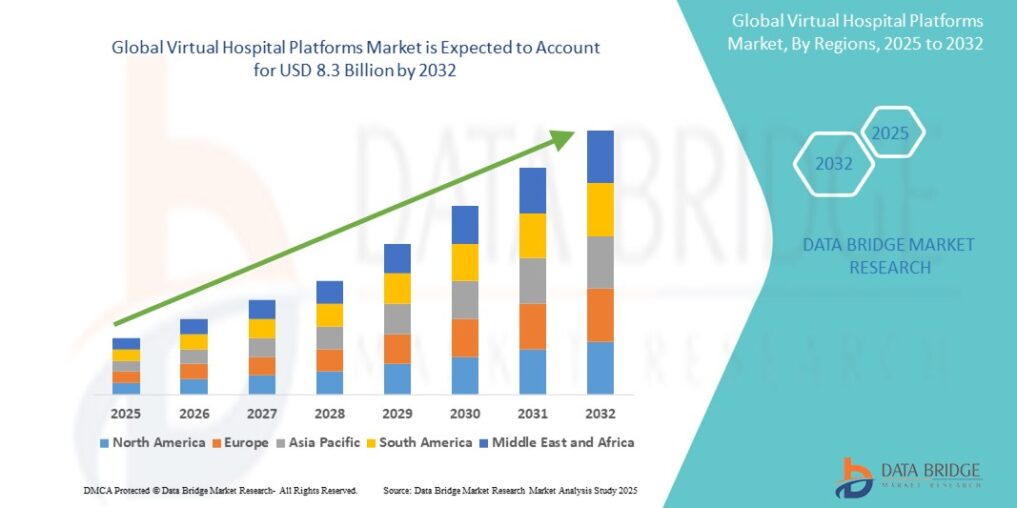
Growth Rate of Virtual Hospital Platforms Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the virtual hospital platforms market was estimated to be worth USD 1.3 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.40% to reach USD 8.3 billion by 2032.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-virtual-hospital-platforms-market
Conclusion
Virtual hospital platforms are no longer a futuristic concept—they are a practical, scalable solution addressing many of the systemic challenges in healthcare today. By bridging physical gaps, enhancing care coordination, and enabling real-time interventions, these platforms are poised to play a pivotal role in the evolution of modern healthcare delivery.