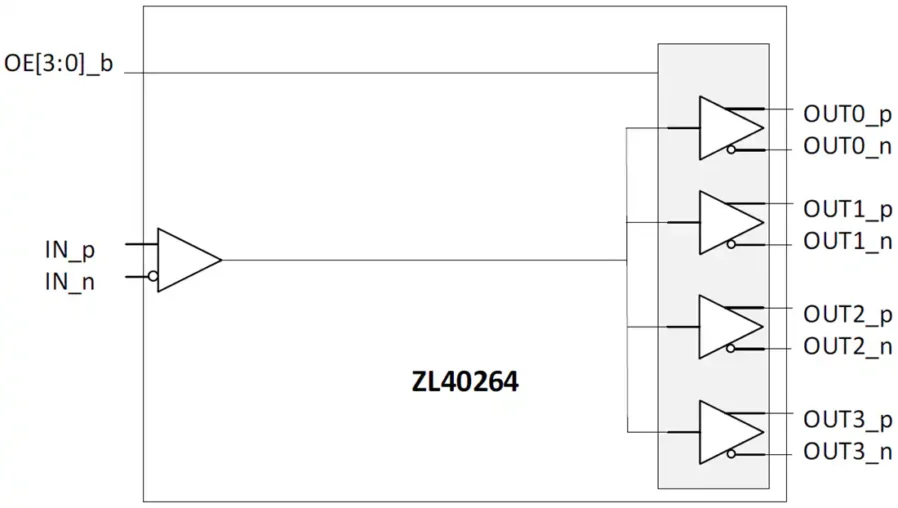
Introduction
A fanout buffer is an integrated circuit designed to take a single input signal and distribute it to multiple outputs while maintaining signal integrity and timing precision. Fanout buffers are widely used in digital systems to ensure synchronized signals across multiple devices.
What is a Fanout Buffer?
Fanout buffers amplify and replicate an input signal to multiple outputs, preventing signal degradation caused by capacitive loading and line impedance. These ICs are critical in high-speed electronics where multiple devices must operate in perfect timing, including processors, memory modules, FPGAs, and communication devices.
Applications of Fanout Buffers
Fanout buffer ICs are commonly applied in:
- Multi-processor server motherboards
- FPGA and ASIC boards
- High-speed memory systems (DDR, QDR)
- Networking and telecommunication hardware
- Consumer electronics requiring synchronized signals
- Industrial automation and control systems
Popular Fanout Buffer IC Models
Some commonly used fanout buffer ICs include:
- CDCLVP111 – Low-skew fanout buffer supporting multiple differential outputs.
- CDCLVP120 – High-speed buffer with LVPECL/LVCMOS interfaces.
- IDT 8T49N240 – Multi-output buffer with programmable delay options.
- SI5338 – Multi-output low-jitter buffer with flexible frequency selection.
- SN65LVDS104 – LVDS fanout buffer for low-noise, high-speed applications.
Comparison Table of Fanout Buffer ICs
| Model | Outputs | Signal Type | Jitter Performance | Typical Applications |
| CDCLVP111 | 4 | LVCMOS/LVPECL | Low skew, low jitter | Servers, embedded computing |
| CDCLVP120 | 4 | LVPECL/LVCMOS | Very low jitter | FPGA/memory systems |
| IDT 8T49N240 | 8 | LVCMOS/LVDS | Low jitter, programmable delay | Networking, telecom |
| SI5338 | Multiple | LVCMOS/LVDS | Ultra-low jitter | Multi-output clock distribution |
| SN65LVDS104 | 4 | LVDS | Very low jitter | Data communication, imaging |
Design Considerations for Engineers
When selecting a fanout buffer IC, consider:
- Number of Outputs – Ensure sufficient channels for all devices.
- Signal Type Compatibility – Match output interfaces with system requirements (LVCMOS, LVDS, LVPECL).
- Jitter and Skew – Choose low-jitter ICs to maintain signal integrity.
- Power Consumption – Important for energy-sensitive or battery-powered systems.
- Package and Layout – Select suitable package and optimize PCB routing to minimize signal degradation.
Conclusion
A fanout buffer is essential for distributing synchronized signals in high-speed digital systems. By selecting the right IC model, engineers can achieve minimal jitter, precise timing, and reliable performance across all connected devices. These ICs are vital for servers, FPGA boards, networking equipment, and high-speed embedded systems.